What Need to Know About Dialysis Access Surgery
Introduction to Dialysis Access
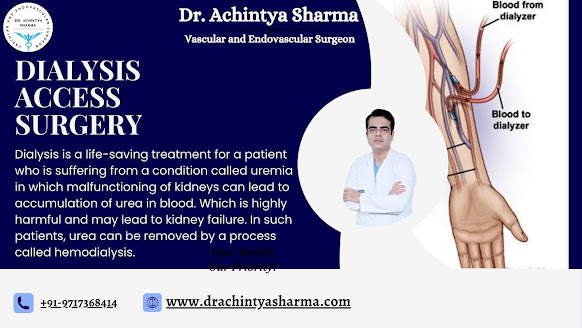
Types of Dialysis Access
Arteriovenous (AV) Fistula: A surgical process in which we connect an artery and a vein in the arm.
Arteriovenous (AV) Graft: A grafted tube interposing under the skin to connect an artery and a vein.
Central Venous Catheter(CVC): A tube placed under the skin and a large central vein in the neck, chest, or groin for temporary access.
Peritoneal Dialysis catheter: A tube placed in the abdominal cavity to permit dialysis fluid to flow in and out of the peritoneal cavity.
Preparing for Dialysis Access Surgery
The best approach is to undergo dialysis access surgery, it is necessary to consult with healthcare professionals to decide the best type of access based on personal needs. Pre-surgery assessment will include blood tests, imaging studies, and conversations about the process. at the time of surgery, patients can hope for local or general anesthesia with the surgical team creating the access site.
Living with Dialysis Access
Regulating life with dialysis access may need daily moderation. Patients with access should maintain proper hygiene, eat healthy food on time, avoid traveling and heavy lifting or pressure on the access site, and follow a suggested diet and fluid intake. proper exercise is encouraged but consult with your health routine provider for guidelines.
Common Complications and Solutions
Infection: proper maintenance and cleaning of the access site and immediately report to your healthcare provider if any sign of infection occurs.
Access Malfunction: observe the signs of decreased blood flow or swelling at the access site and immediately report to the healthcare team.
Blood Clots: Follow the prescription for blood-thinning medications and inform any symptoms of blood clots instantly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dialysis access surgery is a very important step for a person who cannot go for a kidney transplant for some personal and other reasons for the treatment of kidney failure. By understanding the types of access, preparing for surgery, making lifestyle suitable and adjustable for a person, and being conscious of potential complications and difficulties, patients can face the challenges of dialysis with faith and confidence. Always remember to go for regular follow up with healthcare providers or your personal physician for ongoing care and monitoring your health for less risk.
Dialysis surgery requires careful assessment, planning, and skilled surgical techniques to ensure optimal outcomes and minimize complications. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the access site are essential to preserve its function and longevity, enabling patients to receive the life-sustaining dialysis treatment they need.


.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment